A new classification system divides the internal carotid artery into four parts. The vertebral arteries gain access to the cranial vault via the foramen magnum anterolateral to the brainstem.
Blood Supply Of The Central Nervous System Gross Anatomy Of The Brain Part 1
Several branches from the basilar artery originate here and go onto supply the cerebellum and pons.

. Paired vertebral arteries provide blood supply for the upper part of the spinal cord brainstem cerebellum and posterior part of the brain. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system the vertebral arteries provide supply blood to the upper spinal cord brainstem cerebellum and posterior part of brain.
For that reason right half of the brain is supplied by right vertebral and right internal carotid arteries and left half of the brain is supplied by left vertebral and left internal carotid arteries. Lood in the brain is supplied by two pairs of large blood vessels arteries. The entire blood supply of the brain and spinal corddepends on two sets of branchesfrom the dorsalaorta.
Arterial Circle of Willis. These include exostoses such as the retroarticular canal and lateral bridge of the atlas vertebra that may cause compression of the related part of. The parietooccipital artery which supplies part of the cuneus and precuneus the superior occipital gyrus and occasionally the precentral and.
The basilar artery is part of the blood supply system for the brain and central nervous system. It runs behind the carotid artery which is also in the neck. Part of the basal ganglia.
Posteror Cerebral artery supplies. Is the largest branch and the second terminal branch of internal carotid artery. Each artery originates from the first part of the subclavian artery it then courses superiorly along the sides of the neck merging with its companion at the pons level to form the single midline basilar artery.
The carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries. It is usually the larger and more lateral of the two branches of the CCA when visualized with a duplex scanner in a transverse plane. After this the two vertebral arteries converge to form the basilar artery.
It is formed where the two vertebral arteries join at. Brainstem cerebellum part of the spinal cord and part of the cerebrum An ischemic CVA to this branch of the ICA would result in many deficits including impairments to sensory. More often however it keeps going traversing the basilar which has a large diameter and is arrested at the upper bifurcation of the basilar into the.
Concerning the branches each vertebral artery. The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries one on each side of the body then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae C6 or occasionally in 75 of cases at the. It has distinct four segments.
Circle of willis contains-PCA-Posterior Communicating arteries -Internal Carotids -ACA-Anterior Communicating Artery. If the blood supply to the hindbrain via the paired vertebral arteries is reduced sufficiently signs and symptoms of tertebrobasilar ischaemia may result. V1 pre-foraminal arises from the subclavian artery.
The basilar artery terminates by bifurcating into the posterior cerebral arteries. The vertebral arteries and the ten medullary arteriesthat arise from segmental branches of the aorta provide the primary vascularizationof. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery supplies the cerebellum.
These vessels run along the front of the neck. The vertebrobasilar arteries supply the posterior two-fifths of the cerebrum part of the cerebellum and the brain stem. The vertebral artery is among the main arteries which supplies the brain.
The lateral Medulla Posterior and anterior cerebellar. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar artery. The vertebral artery.
There is a right-sided carotid and a left-sided carotid artery. The middle cerebral artery arteria cerebri media is the largest of the carotid arteries that supply blood to the brain 1. Its the first and largest branch of the very first part of the subclavian artery.
If an embolus travels in a vertebral branch it may stop where the vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery. Contributes to the formation of the anterior spinal artery via tributaries that converge in the midline anterior to the medulla oblongata. Where does the vertebral artery go.
The cervical segment 2. V2 foraminal travels alongside vertebral veins and nerves. This artery also supplies blood to the primary sensory and motor areas of the face hand throat and arm 2.
Vertebral artery is one of the main arteries at the base of the neck and is the first branch of the subclavian artery. The vertebral arteriesarise from the subclavianarteries and the internal carotid arteriesare branches of the commoncarotid arteries. At the level of the midbrain the basilar artery bifurcates to form the two posterior cerebral arteries PCA.
The vertebral arteries divide into four segments based on where they are within the spinal column. Which four areas does the Vertebral Basilar System supply blood to. Normally there is little or no mixing of blood between the right and left halves of Circle of Willis.
Gives off a posterior inferior cerebellar artery. There are several factors that may cause a reduction in vertebral artery blood flow. This system provides important areas of the brain with blood.
If a stroke happens in this area it can cause changes with speech vision and sensation. The Internal Carotid Artery ICA It supplies blood to most of the anterior part of the brain. Arises from the common carotid artery Enters the brain at the level of the optic Chiasm.
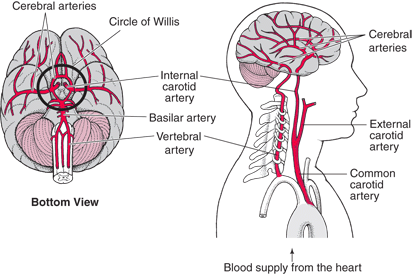
Brain Basics Joe Niekro Foundation

Blood Supply Of The Brain Textbook Of Clinical Neuroanatomy 2 Ed
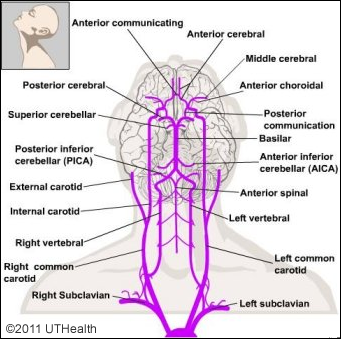
Neuroanatomy Online Lab 4 ƒ3 The Ventricles And Blood Supply Vertebral Basilar System
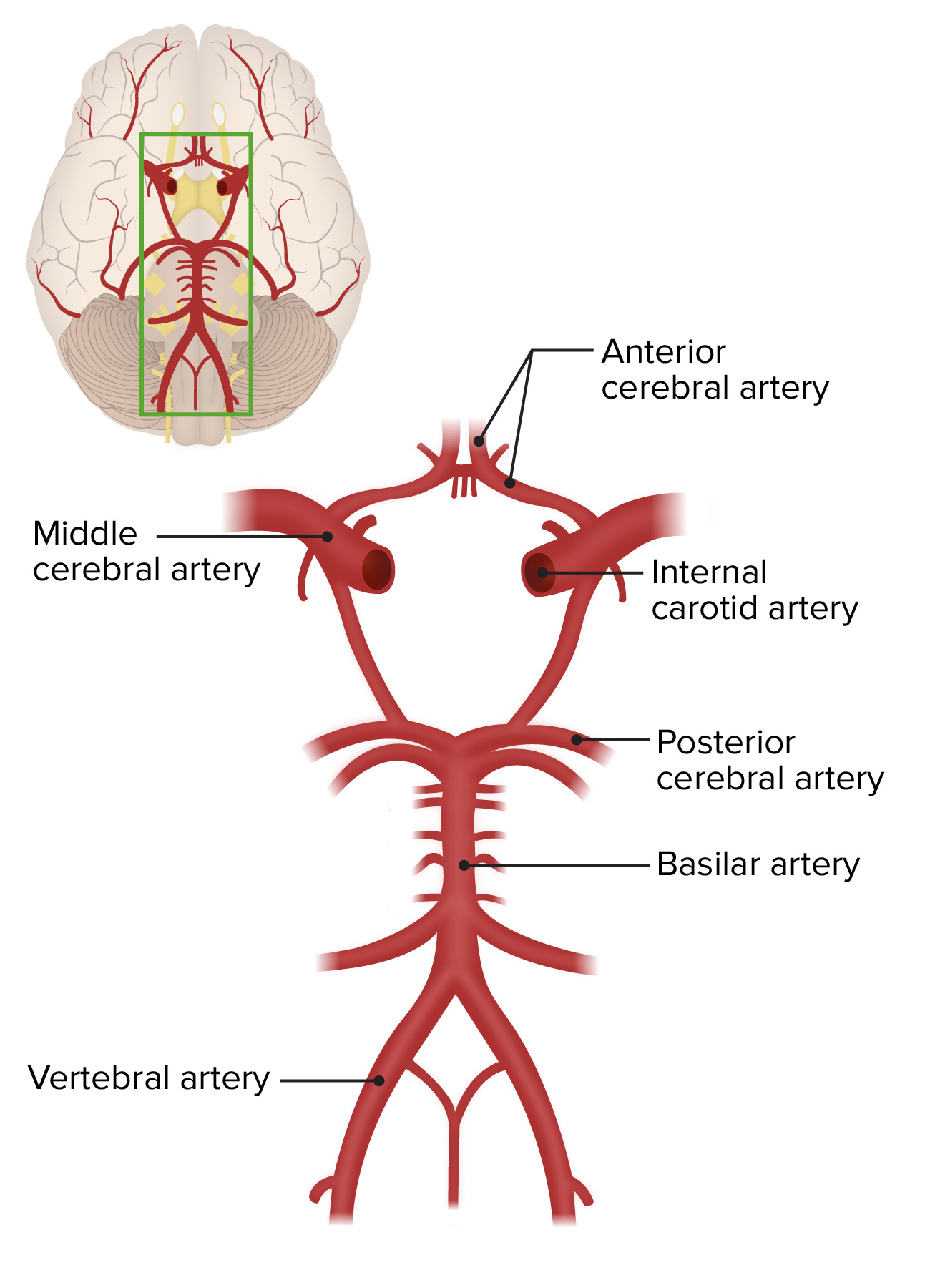
Cerebrovascular System Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
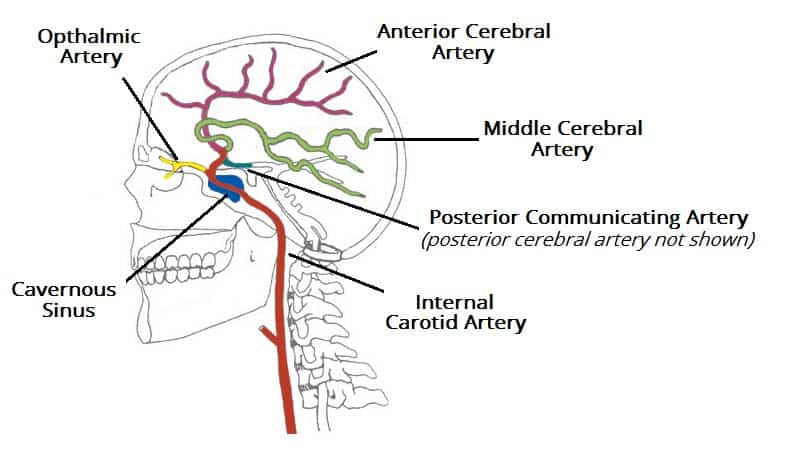
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy
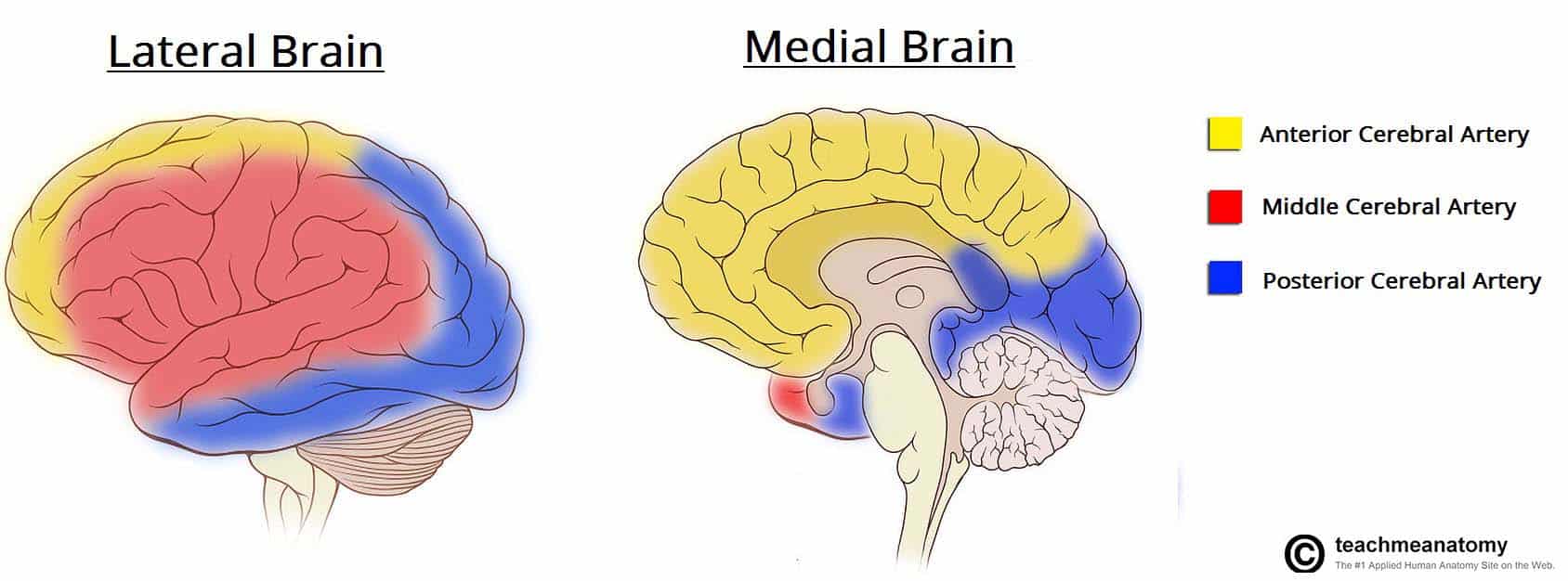
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy


0 comments
Post a Comment